What does HB\HV\HRA\HRC mean in cemented carbide?
In the process of using cemented carbide materials, we often encounter what HB is, what HV is, what HRA is, and what HRC is. So today we will talk in detail about what these models represent.
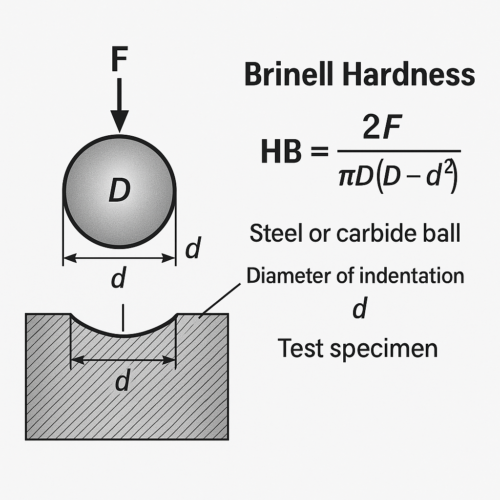
What is Brinell hardness (HB)?
Brinell hardness is a method of measuring the hardness of a material by indentation. It reflects the material’s ability to resist indentation and is mainly applicable to softer metals.
What ranges are applicable to HB Brinell hardness:
Commonly used for: soft metals such as cast iron, copper, aluminum, low carbon steel, aluminum alloys
Not applicable to: high hardness materials such as cemented carbide and ceramics
Advantages: wide measurement range, stable results
Disadvantages: large indentation, not suitable for precision parts or materials with very high surface hardness
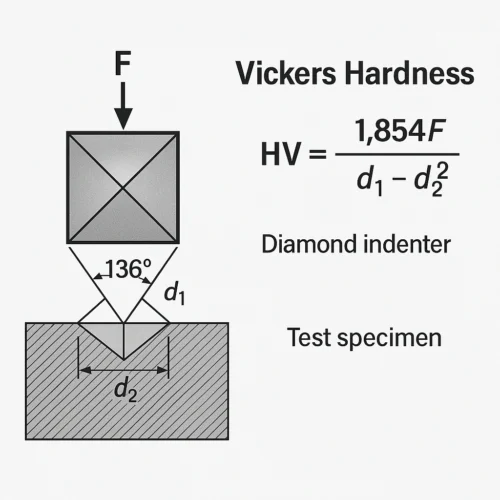
What is Vickers hardness (HV)?
Vickers hardness is calculated by pressing a pyramid-shaped diamond indenter into the material surface under a standard load, and then calculating the hardness value based on the diagonal length of the indentation. It is applicable to materials ranging from very soft to very hard.
Typical HV range in cemented carbide:
Commonly used for: cemented carbide, hardened steel, copper, aluminum
Advantages: high precision, wide application, low damage
What is HRA (Rockwell Hardness A)?
HRA is a measurement standard in Rockwell hardness, specifically used for high-hardness materials such as cemented carbide (such as tungsten steel), thin steel plates, hard coatings, etc. It calculates the hardness value by applying a specific load on the material, pressing a diamond cone indenter into the material surface, and measuring the depth of the indentation.
Explanation of the numerical range of HRA:
| Material Type | HRA hardness range | HRA90+ represents very hard materials, commonly found in high-strength turning inserts or wear-resistant parts |
| Cemented Carbide | 85-94HRA | |
| Ceramic blades | 88-95HRA | |
| Ordinary tool steel | 70-85HRA |
What is HRC (Rockwell C Hardness)?
HRC is a method of expressing the hardness of a material by measuring the depth of an indentation. It is a Rockwell hardness scale (Scale C) and is mainly used to test high-hardness metal materials, especially steel that has been treated after quenching.
Typical HRC values for reference:
| Material Type | Common HRC hardness | Tungsten carbide is too hard to be measured with HRC, otherwise it will damage the diamond indenter. When using cemented carbide, it is recommended to use HRA or HV |
| Annealed steel | 10-20HRC | |
| Medium carbon steel (quenched and tempered) | 30-45HRC | |
| Hardened steel, tool steel | 55-65HRC | |
| White steel knife, high speed steel | 60-67HRC | |
| Carbide (Not applicable) | Not recommended |
HRC is suitable for medium to high hardness metals such as hardened steel and tool steel, but not for cemented carbide. When measuring cemented carbide, please use HRA or HV first.
